Maslow’s Pyramid: what is it, what are its levels, how can we apply it, does it only have advantages?
Our needs move us to overcome every challenge that is thrown our way daily. What is Maslow’s pyramid? What is it for? What are its levels? What are basic needs? What is self-actualization? In this article, we will take a look at Maslow’s hierarchy (or pyramid) of needs more in depth to answer these questions. Discover everything you need to know about motivation through this theory.
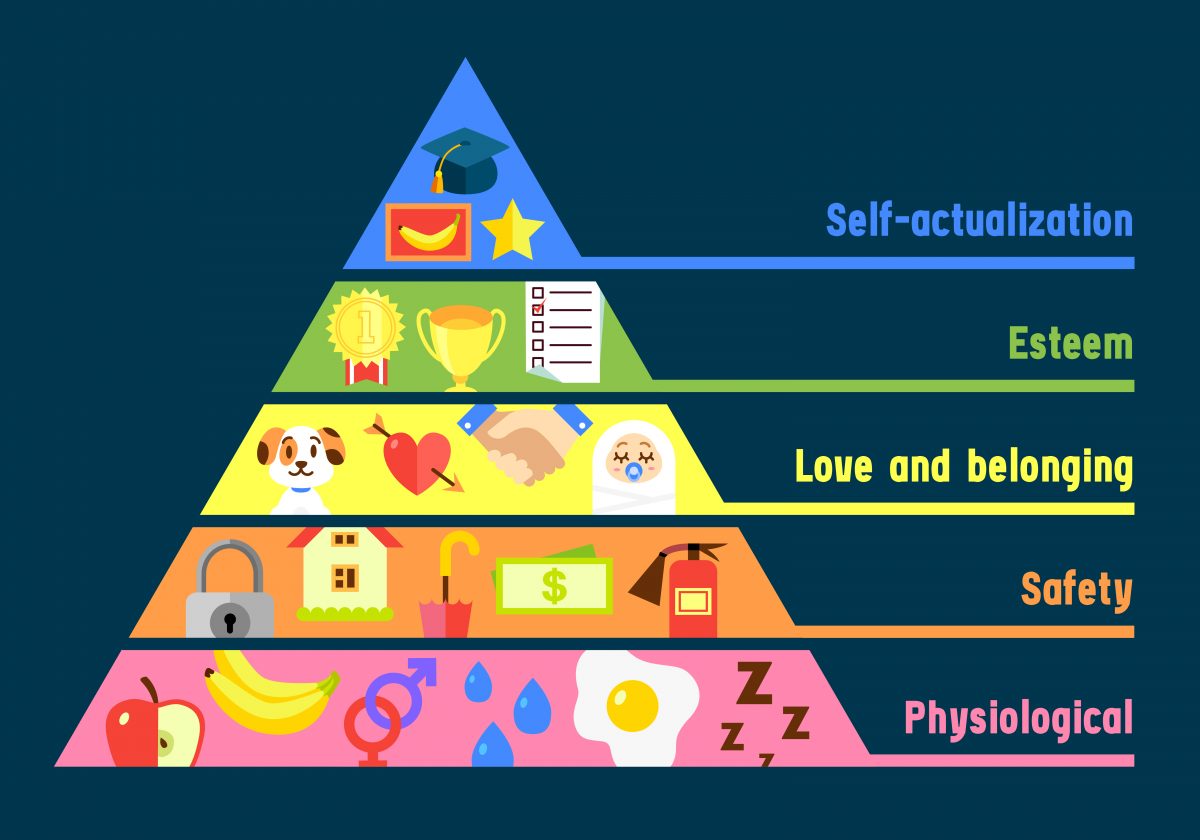
Maslow’s pyramid: hierarchy of human needs.
Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) is the creator of one of the most important motivation theories to this day. This American psychologist researched human needs in order to help people reach their full potential. With his hierarchy of human needs, he revolutionized his field and is still used in different areas of psychology.
Maslow is considered one of the founding fathers of humanistic psychology. This type of psychology explores issues from a philosophical perspective of life in order to answer meaningful questions. It differs greatly from other psychological perspectives, especially behavioral psychology, which only focuses on observable stimuli (like behavior), or from psychoanalysis which focuses on the unconscious.
The humanistic perspective is often criticized for not being entirely scientific. Nonetheless, it’s important that we have different points of view on how to interpret a human being in a holistic point of view.
Maslow believed human needs could be ordered, therefore he created a hierarchy, and with that, a pyramid. Maslow’s pyramid has five levels, the highest level being self-actualization. The way to climb to the top, according to Maslow, is to have an active attitude. Until our basic needs are not met, we can’t climb the next step. We are all responsible for our own progress. Motivation is the key to progressing and moving up.
“What a man can be, he must be. This need we call self-actualization.” Abraham Maslow
Maslow’s Pyramid: Five basic needs
Throughout history, psychology has only focused on the negative aspects of humans, like problematic or impulsive behaviors or mental disorders. However, Maslow decided to center his work around famous figures like Gandhi, Lincoln or Einstein. He analyzed their life in full detail to see how they got to be on top of the pyramid.
This theory is part of a scientific article Maslow wrote called “Theory on human motivation”. Later, his ideas were incorporated into his book Motivation and Personality (1954). Since then, Maslow’s Pyramid has become so famous that even non-psychologists are familiar with it.
His theory is divided into “deficiency needs” (D-needs), which are the first three steps of the pyramid, and “being needs” (B-needs), corresponding to the top two steps of the pyramid. Without meeting the needs of each step, one cannot climb to another step. Only successful and motivated people can reach self-actualization which, whether conscious of it or not, is every human being’s goal.
1. Physiological needs
These needs are the most primal and basic needs for all human beings starting at birth. They are impossible to ignore. They cover actions such as sleeping, breathing, temperature homeostasis, feeding, and mating. Who can ignore when your stomach growls?
These actions help us maintain homeostasis, which is the relatively stable equilibrium in our bodies. According to this theory, if we have severe health problems, it’s less likely we will worry about trivial things. Without thinking outside the box, we have all experienced tiredness or sleepiness. In this state, it is very difficult to concentrate on anything else.
2. Safety needs
This stage is not only about physical safety but also material safety such as:
- Personal security
- Financial security
- Health and well-being
- Safety net against accidents/illness
For example, being fired and not having savings can make this stage very difficult to complete or fulfill.
3. Love and social belonging
This stage holds all of our relationships. We need to have positive and healthy relationships, be it friendship or partners. Love and affection make our existence easier since it involves feelings of belongingness. The group we belong to regardless of size or type (family, friends, sports club, etc.) will always motivate us to make changes and fulfill different stages.
4. Esteem needs
This stage refers to the typical human desire to be accepted and valued by others. It embraces more complex aspects of life such as confidence, trust, self-esteem, respect, and success. Self-esteem is vital for personal growth, a lack of it can lead to inferiority complexes and disorders. If we don’t appreciate ourselves it becomes complicated to worry about anything else, let alone fulfilling all the stages. These needs are usually divided into two:
- Inferior: Based on others’ respect, attention, and appreciation. It’s linked to reputation, status, and position one might have or achieve in society or their social circle.
- Superior: This is based more on ourselves, the self-respect you give yourself. This includes our self-worth, as well as accepting our cognitive skills, thoughts, and emotions.
5. Self-actualization needs
At the top of Maslow’s pyramid is self-actualization. This refers to the mere existence of people and it can only be reached if all the others are satisfied. It is a person’s full potential and the realization of that potential. This stage is driven by creativity, spontaneous actions, morality and no judgments. In this stage, issues can be resolved without duress and reality is seen through positivity.
Not everyone has the same goals, therefore, in order to understand what the ultimate goals are for self-actualization, we need to master the others. For example, one person might feel self-actualization by their very important job at the UN, while another can achieve self-actualization teaching children in a small town. Everyone has different dreams and it doesn’t mean you have to become famous in order to achieve self-actualization.
Maslow, in his later years, criticized his own version of self-actualization, specifying that a human being can find his or her self-actualization in giving themselves to some higher goal outside oneself, in altruism and spirituality. He named this Self-Transcendence, however it was not added to his original pyramid.
“Transcendence refers to the very highest and most inclusive or holistic levels of human consciousness, behaving and relating, as ends rather than means, to oneself, to significant others, to human beings in general, to other species, to nature, and to the cosmos” – Abraham Maslow
Maslow’s Pyramid: Practical applications
In psychology, Maslow’s Pyramid has been studied all around the different perspectives and even been incorporated into practical, day-to-day things.
1. Maslow’s pyramid in organizations and companies.
Public and private institutions require their workers be motivated to work and in turn, they need to know how to motivate their workers. Companies like Google give their workers different benefits apart from the economic ones, in order to keep them motivated to do their job. Companies like Google, Facebook, etc. are leaders in work motivation and keeping efficiency by offering their workers favorable conditions in the workplace. The main reason for this is that if we are happy we are more likely to be motivated and our level of productivity will be higher.
2. Maslow’s pyramid in marketing.
Understanding consumer needs are important for sales to go up and for companies to triumph in a very competitive world. Through publicity and campaign designs, motivation is exploited for effective sales strategies.
3. Maslow’s pyramid in education
Needs accompany us throughout our whole lifetime. Educators need to know in depth the needs of those they are trying to teach. This is important in order to present stimuli that capture their attention.
In order to learn, we need to feel motivated and well. For example, during a war, the main need is survival, while that of knowledge and learning was left to the side. Therefore, any educational plan that doesn’t contemplate the basic needs of the students will fail.
4. Maslow’s pyramid for personal growth
Maslow’s motivational theory lets us know ourselves better. Human needs are common to all, however, we all have personal motivations that in order to be happy we need to discover. Examining our different stages and analyzing them we can contemplate what needs work and from there start our personal progress.

Maslow’s pyramid: self-actualization
Maslow’s Pyramid: Examples
In order to understand Maslow’s motivational theory lets imagine Maslow’s pyramid as steps being climbed by a boy named John. John is an adolescent from an underprivileged neighborhood and an excluded social group.
1. Physiological needs
John is hungry, cold and thirsty. Fortunately, his parents find a job and he starts having access to basic resources.
2. Safety needs
In John’s neighborhood, there are constant gang wars. He is in constant threat of getting hit by a stray bullet or a gang fight. Due to his parent’s new job, they manage to move to a safer neighborhood.
3. Love and social belonging
In his new home, he spends most of his time alone, feeling lonely and sad. Within three months of moving, he makes his high school’s football team and manages to feel accepted and less alone.
4. Esteem needs
John’s first game came and he felt scared to fail or lose or even made fun by his teammates. He feels peer pressure to be the best and even though it was a rough start he starts becoming the star of the football team.
5. Self-actualization needs
As years go by, John makes football a career becoming his state star player. His success allows him to enjoy and reward himself. He has everything wants and his needs are entirely met. Due to his upbringing, he is now capable of seeing the sacrifices that were made for him to have reached self-actualization and is very grateful (this is very important).
Self-actualization has allowed John to now spend his free time on philanthropy. He participates in every charity and meditates every day. This is the perfect example we see in movies of someone that came from nothing and now is fully fulfilled. However, we dont need to imagine such extreme cases. Anyone of us can have difficulties at any stage, the important thing is that we keep a positive attitude and know that with sacrifice and hope we can make it.
Maslow’s Pyramid: Advantages and Disadvantages
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is still a reference when referring to motivation and its importance. However, there are still many critics and its validity is still questioned.
Advantages of Maslow’s motivational theory
- It’s simple: Its approaches can be easily understood and followed by anyone.
- It’s visually pleasing: The pyramid is self-explanatory and very memorable.
- It’s easily aplicable to reality: As you saw in the past example, it’s easy to extrapolate this theory into our daily lives.
- It’s innovative: Maslow’s work was a different, more complete and flexible, perspective from the behaviorism and reductionist perspectives of that time.
Disadvantages of Maslow’s motivational theory
- It’s ambiguous: Needs such as breathing are easily measured, however, concepts such as self-actualization are very abstract. Currently psychology is focusing on scientific perspectives or based on quantifiable evidence. Since this theory is hard to quantify it is considered vague.
- Exaggerated Optimism: Maslow was an optimist and believed in the good nature of humans. He even stated that “when people appear to be something other than good and decent, it is only because they are reacting to stress, pain, or the deprivation of basic human needs such as security, love or self-esteem”.
- Examples that don’t apply: It’s hard to find a theory without exceptions, and this one has many as well. For example, an artist tormented and obsessed by his masterpiece is a perfect example on how sometimes self-actualization might not be satisfactory.
- Other sophisticated theories: There are other theories of motivation based on human needs such as McGregror’s theory (1969) or Alderfer (1972). They were both inspired by Maslow but added more layers and are currently used in human resources department.
Researching what is esential for us in life in order to fulfill our most intimate wishes is important to achieve happiness. It’s certain that this theory will continued to be studied for years to come.
Thank you for reading this article and if you have any questions or want to discuss this further leave a comment below.
This article is originally in Spanish written by Ainhoa Arranz Aldana

